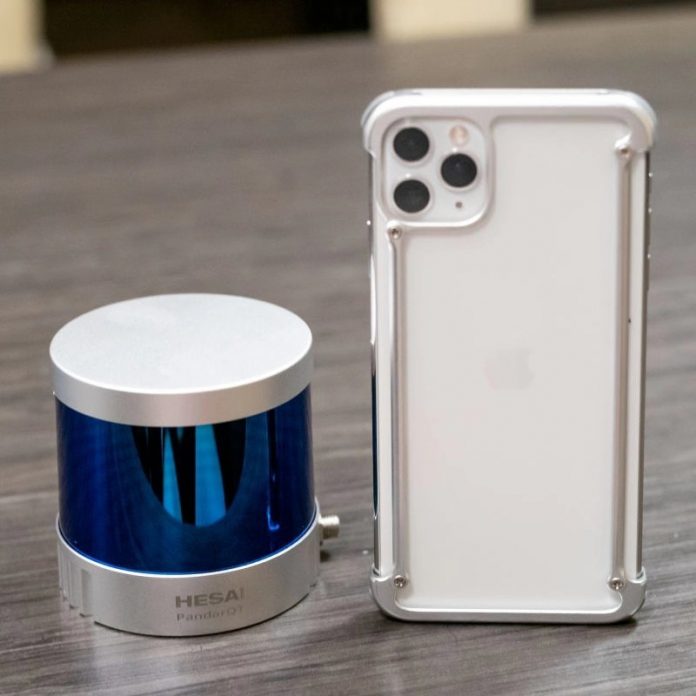
Hesai, a leader in LiDAR sensors, officially unveiled PandarQT at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) in Las Vegas on Tuesday, adding to its portfolio of self-driving sensing solutions.
This 64-channel, ultra-wide FOV LiDAR is the cutting-edge answer to blind spot detection. It features a 104.2° (±52.1°) by 360° ultra-wide Field of View (FOV) which is ideal for vehicle blind spot coverage.
With PandarQT, there is much more than what meets the eye. Apart from its compact and aesthetic design, PandarQT boasts a number of features that contribute to its outstanding performance and reliability. Hesai’s unique interference rejection technology prevents interference from nearby working LiDARs and thus lowers the false detection rate; PTP (Precision Time Protocol) time synchronization is supported to greatly simplify cabling on vehicles. As with all Hesai LiDARs, each PandarQT unit is checked for range accuracy, precision, and other specs before shipping.
Hesai recommends using PandarQT in combination with its flagship product Pandar64. Coupling PandarQT’s short-range capability and Pandar64’s industry-leading long-range performance ensures an all-around and detailed surveillance of a vehicle’s surroundings, near and far.
Blind spot detection: LiDAR’s superiority and the call for optimized design
In the past few years, LiDAR companies have been pushing the specs such as range and resolution, and the market is dominated by long-range LiDARs designed as the centerpiece in a sensor suite. Blind spot detection in the close range has been comparatively neglected. Most companies have misused long range LiDARs, by using them as short range LiDARs, they often have to tilt the LiDARs to “see” low objects on the ground near the vehicle and overhanging objects above the mounting location. To top it all, most budgets are tight, and assigning these expensive long-range sensors to handle short range detection is hard to justify.
That said, reducing the range and thus the cost is not yet the perfect answer to blind spot detection. Many short-range LiDARs have been released on the market at accessible prices, but very few have considered all the necessary merits of being a blind spot LiDAR – wide vertical field of view, excellent short range performance, wide dynamic intensity range to cover both retro reflectors and low reflectivity targets, and a practical range. PandarQT is the right tool for this job.
The design of PandarQT has all these in mind. Hesai has long been planning and perfecting this product, and after a one-year marathon of engineering and thorough testing, it is fully ready to make its debut. At a reasonable price point and with scenario-optimized performance, PandarQT is on its way to become the next industry standard-setting LiDAR.
2020 – a pivotal year for LiDAR development
The year 2020 is a long-awaited inflection point for autonomous driving. The entire auto industry is transitioning to intelligent electric vehicles, and several countries and regions, among them the United States, the EU, Japan, and China, are accelerating the legislation of self-driving road testing, application and safety assurance.
According to Yole Development, the global LiDAR market will reach 6 billion USD in 2024, of which self-driving applications will account for 70%. Hesai has proved its competitiveness on this massive stage, and will continue to develop premium products that meet the industry’s needs, surpass customer expectations, and in the case of PandarQT, fill in the “blind spots” in the market.